|
StableBit CloudDrive
A secure virtual hard drive, powered by the cloud.
|
The Local Cache
(Build 1051)
When you access data on your cloud drive, StableBit CloudDrive will store the most frequently accessed data on one of your local hard drives for faster access. The size of the cache determines how much disk space should be used for caching the data on your cloud drive.
 |
In order to access a large file on your cloud drive, StableBit CloudDrive doesn't need to download the entire file. Instead, only the parts that you need are downloaded and cached. This allows for much faster access to large files such as ISO disk images and large compressed files (e.g. ZIP, RAR, etc...) than would be possible otherwise. The cache in StableBit CloudDrive operates with this in mind, and is able to learn over time and cache not only whole files, but even parts of files that you access most frequently. |
 |
For the best possible performance, use an Enterprise-grade SSD with Power Loss Protection (PLP) as your cache drive. This type of SSD not only provides additional protection against data loss during sudden power failures, but it also significantly enhances the overall performance of your cloud drive due to its non-volatile write cache. When a drive has a volatile write cache (like most consumer SSDs), operating systems need to take additional measures to ensure data consistency. These measures can significantly impact your SSD's performance, depending on the workload. |
If you'd like, you can set the local cache size to the Minimal setting in order to maintain the smallest possible cache size.
When the cache is set to Minimal, reads will only be cached momentarily and writes will be cached until they can be fully uploaded to the storage provider.
 |
If Metadata Pinning is enabled, then file system metadata will remain in the cache (for supported file systems), even if a Minimal cache size is set. |
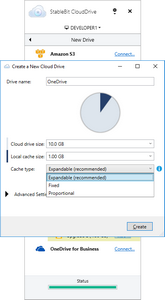
StableBit CloudDrive supports 3 different cache types:
-
Expandable
-
Fixed
-
Proportional
In order to illustrate the differences between them, let's imagine that you have a 500 GB drive with some data on it, and that you've chosen to use a 100 GB cache for your cloud drive, like so:

Here's how the different cache types will utilize the local cache:
-
Expandable (recommended):
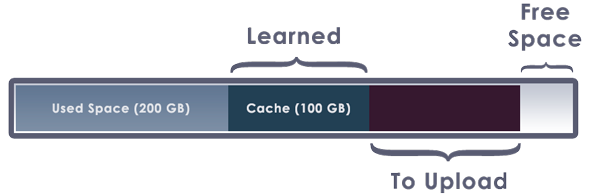
Over time, an expandable cache will learn what data is accessed most often and it will cache that data locally, up to the selected cache size limit.
Any data written to the drive will expand the cache and use up additional disk space on the cache disk. Once uploading finishes, the written data will be cleared from the cache and the cache will shrink to its original size.
This is the recommended cache type for optimal drive and system performance.

An expandable cache will try not to consume all of the disk space on the local cache drive. It will always try to keep at least 5 GB free. As the free space on the cache drive approaches 5 GB, in order to continue to maintain some free space on the local cache drive, writes to the cloud drive will get progressively slower.
As your uploads make progress, the uploaded data will be cleared from the local cache in order to make room for new data to be written to your cloud drive.
If your uploads are not making any progress (perhaps due to a networking issue), and the free space on your local cache drive falls below 5 GB, in order to prevent the cache drive from completely running out of disk space, any additional write requests to the cloud drive will fail.
-
Fixed:
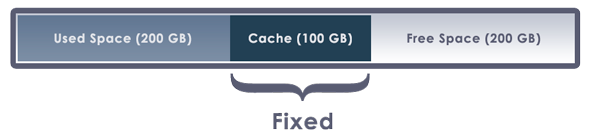
A fixed sized cache will not grow beyond the selected size limit.
Any data written to the drive will overwrite locally cached data.

Because of this, a fixed sized cache limits the drive's ability to learn to cache the most frequently used data locally.
If a fixed sized cache becomes full, any additional writes to the cloud drive will be throttled.
-
Proportional:

A proportional cache will split the cache into 2 parts. One part will be used for caching reads and the other part will be used for caching writes.
Like an expandable cache, this type of cache is good at caching the most frequently used data locally. While at the same time, the cache can be limited to only use a certain amount of disk space.
When the write cache is not in use, it will be used for read caching.
 |
For more in-depth information about the cache types, see our blog post at: https://blog.covecube.com/2016/12/stablebit-clouddrive-1-0-0-777-beta/ |